
Unit 1.5
Active Learning Strategies for the Classroom and Online Resources
NLN Competency: I
Objectives
- Learners will define the theoretical origins of active learning.
- Learners will recognize the benefits of active learning and identify learning assessment
strategies. - Learners will associate teacher preparation and personal reflection to active learning
strategies.
Introduction
This module aims to identify resources and provide instruction for educators to expand the understanding and implementation of active learning theory in the classroom utilizing online resources.
Active Learning
Active learning (AL) is based on a theory called constructivism. A philosophy based on the concept that people construct their own understanding by reflecting on their personal experiences and by relating the new knowledge with what they already know. Individuals create their own mental models, known as ‘schemas’, to make sense of the world. Individuals accommodate new knowledge by adjusting their ‘schemas’ (Cambridge Assessment International Education, n.d.). AL is a process with student learning at its center by focusing on how students learn, not just on what
they learn. Students are encouraged to ‘think hard’ rather than passively receive information from the teacher (Cambridge Assessment International Education, n.d.). Similarly, John Dewey (1916) argued that education and learning are social and interactive processes…he believed that students thrive in an environment where they are allowed to experience and interact with the curriculum, and all students should have the opportunity to take part in their own learning.” A compilation of theories provides an overview of active learning that includes: learning is developmental, and content should be relevant and within a meaningful context.
Benefits of Active Learning
- Active learning helps students to become ‘lifelong learners.’
- Active learning encourages success because students draw on their understanding in order to evaluate and synthesize ideas, thereby enhancing skill and understanding.
- Active learning is engaging and intellectually exciting.
- Active learning can be implemented with online resources and interactive web sites as well as the traditional classroom setting.
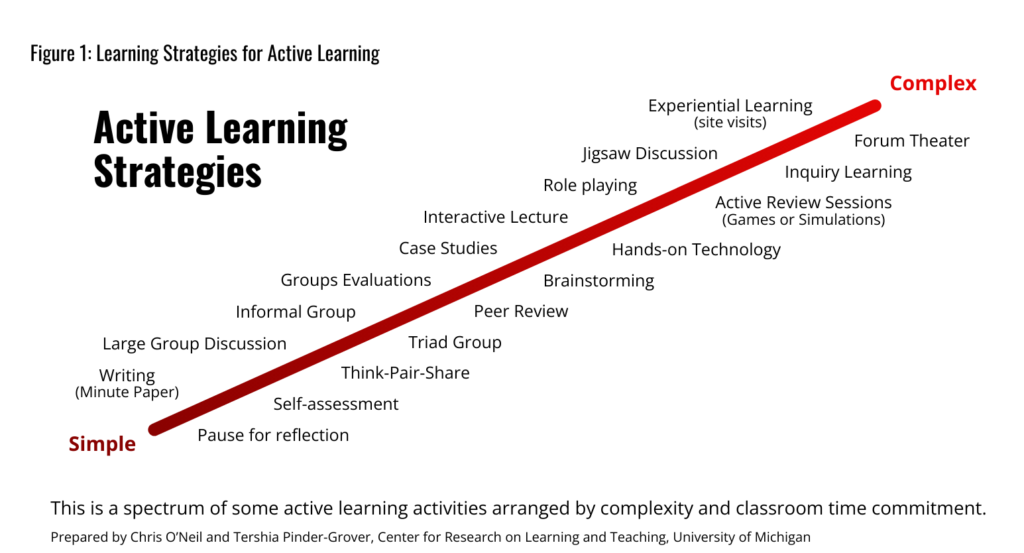
Note. How can you incorporate active learning into your classroom? by C. O’Neal and T. Pinder-Grover, n.d.,from Center for Research on Learning and Teaching, University of Michigan.
https://crlt.umich.edu/sites/default/files/resource_files/02_Active%20Learning%20Continuum.pdf
Assessment of active learning strategies include written and oral debriefing, observations, peer- and self-assessment, and presentations and demonstrations.
Conclusion
Active learning is based on the concept that people construct their own understanding by reflecting on their personal experiences and by relating the new knowledge with what they already know. It is engaging and intellectually exciting and can be implemented with online resources and interactive web sites as well as the traditional classroom setting.
References
Cambridge Assessment International Education. (n.d.). Getting started with active learning. https://www.cambridge-community.org.uk/professional-development/gswal/index.html
Dewey, J. (1916). Democracy and education: An introduction to the philosophy of education. New York: Macmillan.
Gibson, K., & Shaw,C.M., (2020). Assessment of active learning. https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190846626.013.120
Giddens, G., Caputi, L., & Rodgers, B. (2020). Mastering concept-based teaching: A guide for nurse educators (3rd ed.). St. Louis, Missouri: Elsevier
McGill University. (2014). Strategies to support active and collaborative learning. https://und.edu/academics/ttada/_files/_docs/active-learning-strategies.pdf
O’Neal, C., & Pinder-Grover, T. (n.d.). How can you incorporate active learning into your classroom? Center for Research on Learning and Teaching, University of Michigan https://crlt.umich.edu/sites/default/files/resource_files/02_Active%20Learning%20Continuu
m.pdf
Author: Vicky A Keys,DNP, MSN, RN-BC, ACNS-BC
Go to Unit 1.4 Go to Unit 2.1